Introduction
In the grand picture of engineering projects, the anti – corrosion issue of metal structures is like a cornerstone, supporting the stability and durability of the entire project. According to authoritative statistics, the global economic losses caused by corrosion reach tens of billions of dollars every year. These losses are not only reflected in the maintenance and replacement costs of infrastructure but may also lead to serious safety accidents, posing a huge threat to people’s lives and property. Zinc rich primers, as widely used coatings in the field of metal structure anti – corrosion, are divided into two main types: organic and inorganic. Understanding the differences between them is crucial for customers with engineering projects to select the appropriate primer, improve the anti – corrosion effect of the project, and enhance economic benefits.
Understanding Zinc Rich Primers
Zinc rich primer is a kind of coating containing a large amount of zinc powder, which provides cathodic protection for metal substrates such as steel. According to the different binders used in the primer, it can be divided into organic zinc rich primer and inorganic zinc rich primer. Organic zinc rich primers usually use organic resins such as epoxy resin as binders, which endow the primer with flexibility and adhesion. Inorganic zinc rich primers use inorganic materials such as ethyl silicate as binders, having unique performance characteristics. Both have their own advantages and application scenarios.

Organic Zinc Rich Primers
Composition and Characteristics
Organic zinc rich primers use organic resins (such as epoxy resin, polyurethane, alkyd resin, etc.) as the main film – forming substances, and usually contain more than 77% zinc powder. Their advantages include good construction performance, being able to be constructed under low – temperature and humidity conditions, fast drying speed, and excellent flexibility and impact resistance. However, they have poor heat resistance, chemical resistance, and weather resistance.
Advantages in Engineering Projects
With good construction performance, organic zinc rich primers are suitable for complex construction environments. In projects with high appearance requirements, they can provide good decorative effects and can adapt to the deformation and vibration of metal structures, ensuring the safety of the structures.
Limitations and Considerations
Due to their poor weather resistance, organic zinc rich primers need to be paired with weather – resistant topcoats when used outdoors. When selecting, the zinc powder content and organic resin type should be chosen according to the project and environmental conditions. They are relatively expensive and contain organic solvents, so ventilation and protection should be paid attention to during construction and use.
Inorganic Zinc Rich Primers
Composition and Characteristics
Inorganic zinc rich primers use inorganic materials such as ethyl zinc silicate primer as binders, and usually contain more than 80% zinc powder. They have advantages such as high heat resistance and good chemical resistance, but are hard and brittle, and have strict requirements for steel surface treatment.
Advantages in Engineering Projects
Inorganic zinc rich primers are suitable for high – temperature and high – corrosion environments such as petrochemical, power, and metallurgy industries, as well as the marine engineering field. They can provide long – term anti – corrosion protection, have good weather resistance and wear resistance, and can reduce operating costs.
Limitations and Considerations
Inorganic zinc rich primers have high construction requirements and are sensitive to the environment, with poor recoating performance. They are expensive and have high construction costs. They are brittle and prone to cracking when subjected to external impact, so protection measures are needed.
Comparison between Organic and Inorganic Zinc Rich Primers
Anti – corrosion Performance
In general, inorganic zinc rich primers are superior to organic ones. In salt spray tests, inorganic zinc rich primers have a longer salt – spray resistance time. However, in mild corrosion environments, organic zinc rich primers can also meet the anti – corrosion requirements when paired with suitable topcoats. Their flexibility can buffer impacts and improve the anti – corrosion performance.
Adhesion and Coating Integrity
Organic zinc rich primers have good adhesion, low requirements for surface roughness, and good flexibility. Inorganic zinc rich primers have stronger adhesion but strict requirements for surface treatment. They are brittle and prone to cracking when impacted.
Construction and Curing
Organic zinc rich primers are easy to construct, have low environmental requirements, fast drying speed, and various construction methods. Inorganic zinc rich primers have high construction requirements, need to control temperature and humidity, have a slow drying speed and long curing time, and are usually applied by spraying.
Cost – effectiveness
Organic zinc rich primers have low prices and construction costs. Inorganic zinc rich primers are more expensive and have higher construction costs, but they have better anti – corrosion performance and a longer service life, so their long – term cost – effectiveness may be higher.
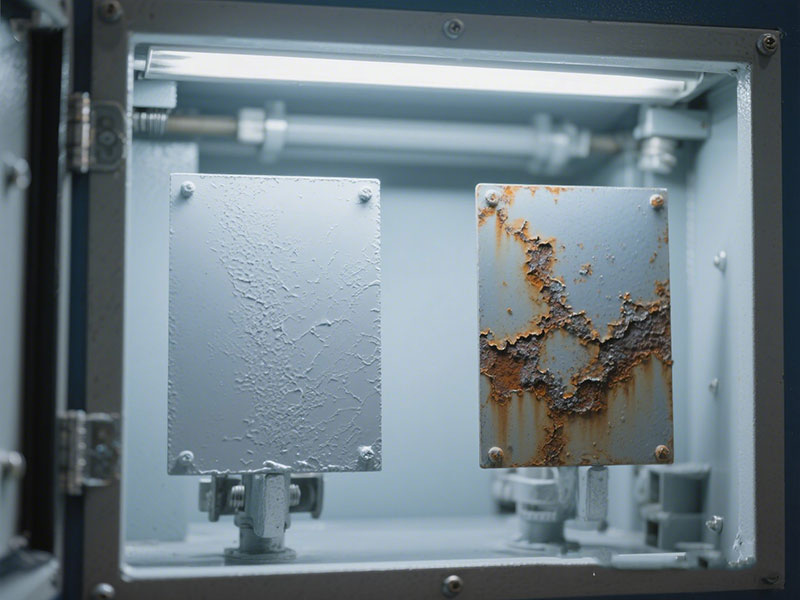

Factors to Consider When Choosing Zinc Rich Primers
Project Requirements
The usage environment, anti – corrosion service life, and structure type of the project should be considered. For high – temperature and high – corrosion environments, inorganic zinc rich primers are a better choice. For projects with high requirements for construction efficiency and cost and relatively mild corrosion environments, organic zinc rich primers are more suitable. The compatibility with topcoats, weldability, and wear resistance of the primer also need to be considered.
Environmental Conditions
Different environments have different performance requirements for primers. For example, in high – temperature environments, heat – resistant primers such as jotun zinc rich epoxy primer should be selected; in humid environments, water – resistant primers are needed. Environmental factors such as humidity and pH affect the construction and curing of primers, so the primer type and construction technology should be selected according to local environmental conditions.
Budget Constraints
The cost – performance ratio of the primer should be considered according to the project budget. If the budget is limited, organic zinc rich primers can be selected. If the budget is sufficient and high anti – corrosion performance and long service life are required, inorganic zinc rich primers are a better option. At the same time, the construction cost, including surface treatment cost, construction technology cost, and curing time cost, also needs to be considered.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
In summary, organic zinc rich primers have good construction performance, low requirements for surface treatment, and relatively low prices, but relatively weak anti – corrosion and heat resistance. Inorganic zinc rich primers have excellent anti – corrosion and heat resistance, are suitable for harsh environments, but have high construction requirements and relatively high prices. When choosing, factors such as project requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints should be comprehensively considered.
Recommendations for Engineering Project Customers
Customers with engineering projects are advised to consult professional coating suppliers or anti – corrosion experts to understand the characteristics and application ranges of different types of primers. The selection of primers should be considered at the project design stage. During construction, the construction instructions should be strictly followed. For inorganic zinc rich primers, surface treatment and environmental control should be emphasized. For organic zinc rich primers, attention should be paid to the compatibility with topcoats and construction technology. Regularly inspect and maintain the coating, and keep an eye on the development trends in the coating industry.
Future Trends in Zinc Rich Primer Technology
Zinc rich primer technology is developing towards high – performance, environmental – friendly, and intelligent directions. In terms of high – performance, primers with self – repair functions may be developed. In terms of environmental protection, there will be a greater emphasis on reducing the emission of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and using water – based and other environmentally friendly formulations. In terms of intelligence, primers may have monitoring and early – warning functions.