7 Expert Steps to Prevent Thermal Shock Damage in Food Processing Floors
Thermal shock damage in food processing floors is best prevented by specifying and correctly installing a thick, seamless Cementitious Urethane (Urethane Concrete) system, which matches the thermal movement of the underlying concrete slab. The most effective strategy involves selecting a high-performance material like polyurethane cement, ensuring meticulous substrate preparation, and detailing critical areas such as drains and joints to maintain a robust, monolithic seal. This comprehensive approach is essential for achieving a durable, hygienic flooring system that withstands continuous thermal cycling and the aggressive conditions of daily washdown areas.
1. Why is Thermal Shock the Primary Cause of Floor Failure in Food Plants?
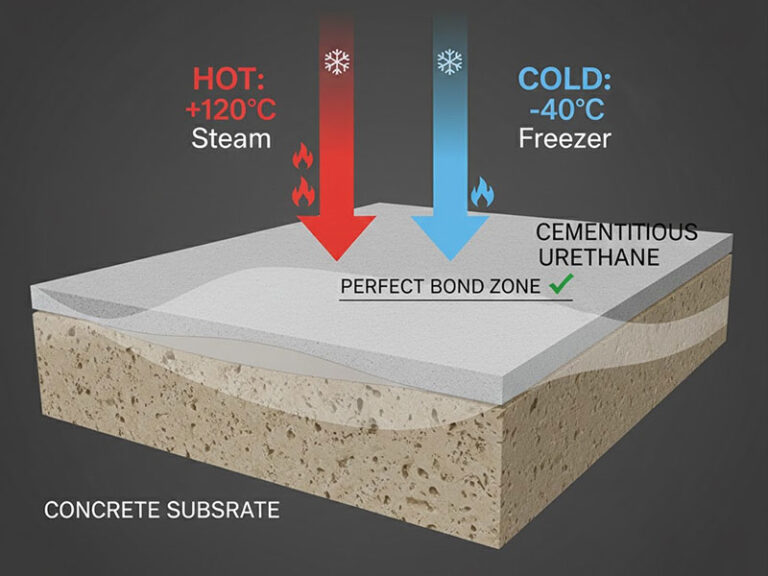
Thermal shock occurs when rapid, extreme temperature fluctuations cause differentialexpansion rates between the floor coating and the concrete substrate. Standard coatingssuch as thin-film epoxies, possess a different coefficient of thermal expansion (a) comparedto concrete. When a cold floor (e.g., 4°C’ in a freezer) is rapidly cleaned with 95°C’ steam, therigid epoxy expands quickly while the concrete reacts slowly. This disparity creates intensetensile and shear stress at the bond line, leading to the two most common forms of failure:floor delamination (peeling) and floor cracking.
- Principle Explained: The stress (σ) generated by temperature change (ΔT’) isproportional to the difference in the material’s thermal expansion coefficient and itselastic modulus (E). Rigid materials like standard epoxy cannot absorb this stress.
- Source Citation: According to the USDA and various food and beverage processingstandards, floors must withstand daily cleaning procedures, which often involve steam orhot water well above 82°C’ (180°F’), making high thermal resistance non-negotiable.
2. Choosing the Right Material: Why Urethane Concrete is the Gold Standard
Cementbaserad uretan (also known as Polyurethane Cement or Ucrete) offers the highest resistance to thermal shock among resinous flooring options because its thermal expansion coefficient closely matches that of concrete. This similarity allows the coating and the slab to expand and contract together harmoniously, dramatically reducing stress at the bond line and virtually eliminating the risk of floor delamination.
Urethane Concrete vs. High-Temperature Epoxy Comparison
While some high-temperature epoxy systems offer improved performance over traditional epoxies, they generally cannot match the durability of polyurethane cement in sustained, extreme thermal cycling environments.
| Funktion | Cementbaserad uretan | Standard Epoxi | High-Temperature Epoxy |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Excellent (Designed for-40°C to 120°Cexposure) | Poor (Prone tofailure above65°C) | Fair to Good (Improved formulation, but often more rigid than PU Cement) |
| Tjocklek | High (Typically 6mm to 9mm) | Low (Typically 2mm to 4mm) | Medium (Typically 4mm to 6mm) |
| Expansion Match to Concrete | Very High (Closely matches) | Låg | Måttlig |
| Recommended Use | Washdown areas, Freezers, Ovens, Food Plant Floor Damage prevention | Dry production, light traffic | Areas with periodic hot water, but not steam |
3. Essential Substrate Preparation for a Reliable Bond
A durable, thermal shock-resistant floor system is impossible without correct concrete substrate preparation, as adhesion failure is the root cause of most floor failure. The goal is to achieve an appropriate Concrete Surface Profile (CSP) and mitigate potential moisture issues.
- The Problem: Residual contaminants, surface laitance (a weak layer of cement paste), or high moisture vapor transmission rate (MVT) will prevent a strong chemical bond, leading to premature floor delamination.
- The Solution (Step-by-Step):
- Mechanical Abrasion: The concrete must be mechanically prepared, typically via shot blasting or heavy diamond grinding, to achieve a CSP-3 to CSP-5 profile as per the International Concrete Repair Institute (ICRI) standards.
- Fuktprovning: Before application, the slab must be tested. Most resinous materials require the relative humidity (RH) inside the concrete to be below 80%. If RH is high, a dedicated moisture vapor barrier or mitigation system must be applied.
- Repair: All existing floor cracking and spalling must be repaired with an epoxy or polymer repair mortar before the main Coating is applied.
4. Managing Critical High-Stress Areas: Joints and Drains
High-traffic and critical termination points, specifically expansion joints and floor drains, are the most frequent sites of floor failure and must be properly detailed to anchor the seamless flooring.
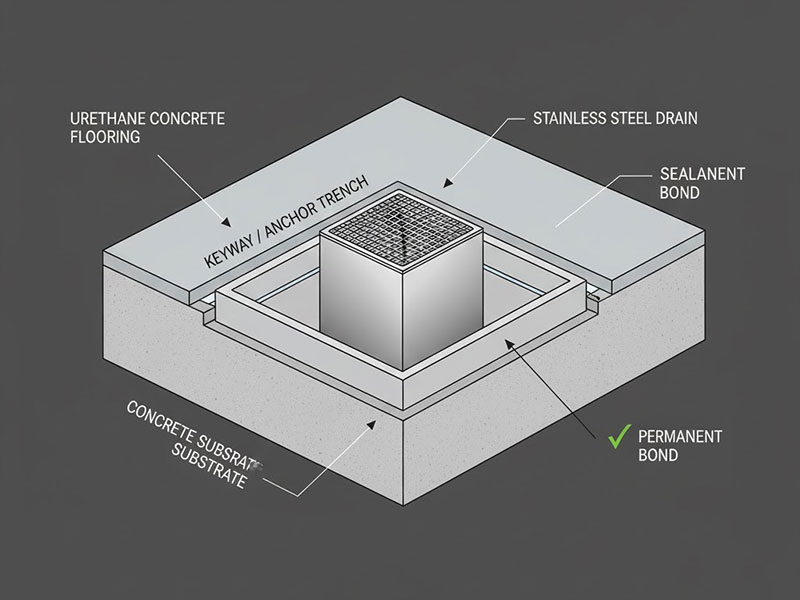
Why Keying Prevents Floor Delamination at Drains
To prevent the edge of the resinous flooring from lifting or being undercut by aggressive cleaning, a mechanical anchor is required around drains and perimeter trenches.
- Genomförande: The contractor must cut a small trench or groove (keyway or anchor trench) around the entire perimeter of the drain. The urethane concrete flooring material is then poured into this keyway, effectively locking the coating down and preventing lateral movement caused by thermal stress.
- Standard: The depth of the keyway should be at least 6mm (0.25 inches), matching the thickness of the floor system.
[Diagram of a keyed anchor trench detail around a floor drain to prevent floor failure.]
5. Application Thickness: The Critical Factor for Durability
The applied thickness of the cementitious urethane system directly correlates with its ability to withstand thermal stress and heavy impact in industrial flooring environments. A thicker application acts as a superior insulator, reducing the speed and intensity of heat transfer to the concrete slab below.
- Standard Recommendation: For areas with light to moderate cleaning, a 6mm (1/4 inch) thickness is usually acceptable.
- Extreme Thermal Cycling: For high-heat areas, such as direct steam-cleaning zones, kettle areas, and cooker stations, a thickness of 9mm (3/8 inch) or even 12mm is highly recommended to provide maximum insulation and resilience against thermal cycling.
6. Maintenance and Operational Best Practices
While the material selection is key, minimizing the rate of temperature change during daily operations further protects the seamless flooring system from long-term thermal stress.
- Gradual Temperature Changes: If possible, implement a cooling period before starting high-temperature washing. For example, allow a hot production area to cool down naturally for 10-15 minutes before introducing washdown water.
- Cleaning Temperature Control: Calibrate cleaning equipment to avoid applying steam or water above the manufacturer’s specified limit for the polyurethane cement system (typically 100°C -120°C).
- Avoid Localized Hot Spots: Train personnel to avoid directing high-pressure, high-temperature steam directly at a single spot on the floor for extended periods, as this can cause localized thermal stress and premature floor failure.
7. Ensuring Regulatory Compliance: FDA and Hygienic Flooring
The selection of a thermal shock-resistant system is also a prerequisite for maintaining a truly FDA compliant flooring system and meeting critical food safety standards.
- Hygienic Requirement: Because urethane concrete flooring is applied seamlessly and withstands the aggressive cleaning necessary to eliminate pathogens, it prevents the cracks, fissures, and delamination where bacteria (such as Listeria och Salmonella) can harbor. Floor delamination creates unreachable pockets, making a facility non-compliant.
- Authority Reference: The FDA and GFSI (Global Food Safety Initiative) standards implicitly require non-porous, durable, and easily cleanable surfaces, directly necessitating a coating with high chemical and thermal resistance like polyurethane cement.
Authoritative Reference & Expertise Statement
This article was written by a content specialist with expertise in industrial flooring, specializing in food and beverage processing environments. The recommendations are based on ICRI (International Concrete Repair Institute) standards and material science data specific to thermal stress on polymer coatings.
Author: [Jason Zhang., Senior Industrial Flooring Consultant]
Date Last Updated: December 2025
KAIDA PAINT Brand Advantage Statement
KAIDA PAINT is a leading manufacturer of high-performance industrial flooring solutions, specifically engineered to meet the extreme demands of the food and beverage processing sector. Our flagship Urethane Concrete Flooring systems, formulated with advanced polyurethane cement technology, are designed to endure aggressive high-temperature washdowns and severe thermal cycling—the primary causes of floor delamination. As a trusted manufacturer, we offer proven systems that ensure your facility achieves a truly seamless flooring and FDA compliant flooring surface, minimizing the risk of floor failure and maximizing operational uptime. Contact a KAIDA PAINT Contractor today for a consultation on your food processing floor project.